Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is essential for overall well-being. Blood sugar, or glucose, is a critical source of energy for the body's cells, but it must be kept within a certain range to prevent health issues. This blog post will delve into the importance of blood sugar levels, how they are regulated, the impact of diet and lifestyle, and how to manage and monitor them effectively.

The Basics of Blood Sugar
What is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar refers to the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar derived from the foods we eat, primarily carbohydrates. It serves as a primary energy source for the body's cells and is crucial for normal functioning.
How is Blood Sugar Measured?
Blood sugar is typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) in the United States and millimoles per liter (mmol/L) in many other countries. Normal fasting blood sugar levels usually range from 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L). Levels that are consistently higher or lower than this range may indicate health issues that require attention.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Regulation
Maintaining proper blood sugar levels is vital for several reasons:
- Energy Supply: Glucose is the main energy source for the body, especially the brain, which relies on a steady supply to function correctly.
- Metabolic Health: Proper regulation of blood sugar helps maintain metabolic balance and prevents conditions like insulin resistance.
- Long-term Health: Chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision problems.
How Blood Sugar is Regulated
The body has a complex system for regulating blood sugar levels, involving several organs and hormones:
- Insulin and Glucagon: The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, two hormones that play key roles in blood sugar regulation. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood sugar levels. Glucagon, on the other hand, stimulates the release of glucose from the liver, increasing blood sugar levels when they are too low.
- The Liver: The liver acts as a storage site for glucose in the form of glycogen. When blood sugar levels drop, the liver breaks down glycogen into glucose and releases it into the bloodstream.
- Muscles and Fat Cells: Muscle and fat cells also store glucose and respond to insulin by absorbing glucose from the blood.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Carbohydrate intake has the most direct impact on blood sugar levels. Simple carbohydrates (sugars) can cause rapid spikes, while complex carbohydrates (starches) lead to more gradual increases. Protein and fat also affect blood sugar but to a lesser extent.
- Physical Activity: Exercise increases the body's sensitivity to insulin, helping lower blood sugar levels. It also helps muscles absorb glucose for energy.
- Stress: Physical and emotional stress can cause the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which increase blood sugar levels.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep can disrupt the regulation of blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and some blood pressure drugs, can affect blood sugar levels.
- Illness: Infections or illnesses can raise blood sugar levels due to the body's stress response.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels and Diabetes
Diabetes and Prediabetes
Diabetes is a condition characterized by chronic high blood sugar levels. There are two main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin. It is often associated with obesity and lifestyle factors and can sometimes be managed with diet and exercise alone.
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is a significant risk factor for developing Type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of High and Low Blood Sugar
- High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores. Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to severe complications.
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, confusion, irritability, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness. It requires immediate treatment, typically with fast-acting carbohydrates.

Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for people with diabetes and can be beneficial for those at risk. There are several methods for monitoring blood sugar:
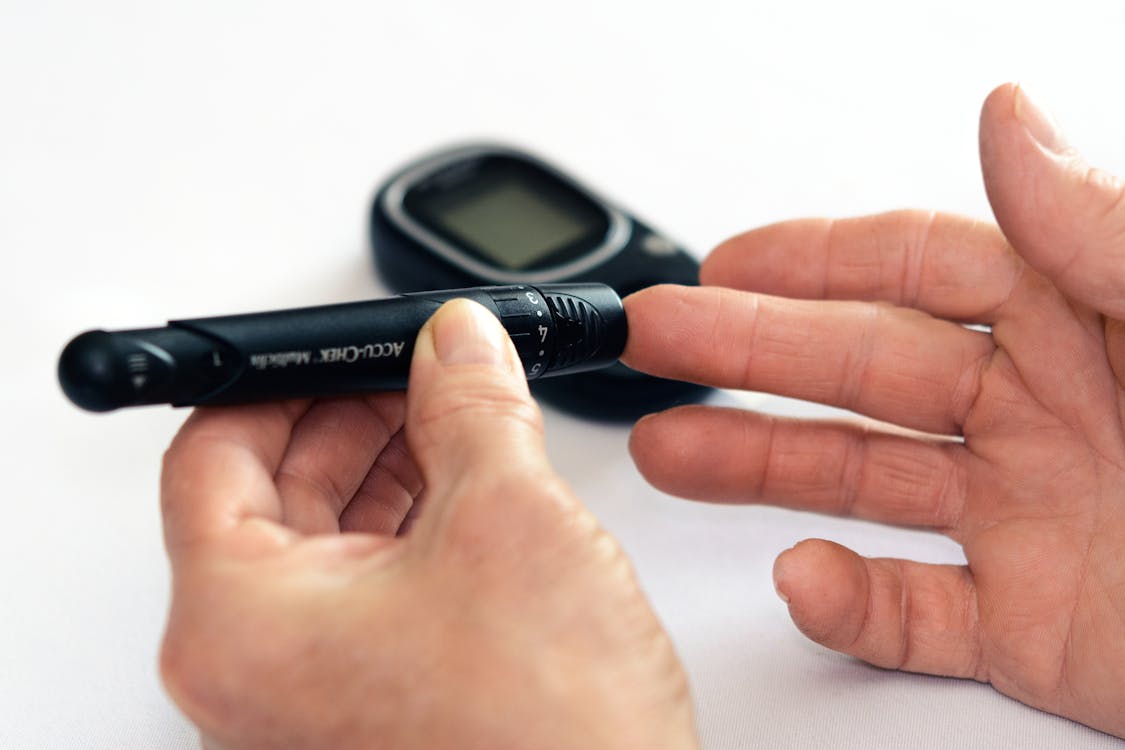
- Fingerstick Blood Sugar Testing: Using a glucose meter, individuals can prick their finger to obtain a drop of blood and measure glucose levels. This method provides immediate results and is useful for daily monitoring.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): CGMs are wearable devices that continuously monitor blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. They provide real-time data and can alert users to high or low blood sugar levels.
- A1C Test: The A1C test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It is a valuable tool for assessing long-term blood sugar control and is typically used in conjunction with daily monitoring.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Diet and Nutrition
- Balanced Meals: Eating a balanced diet with a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Focus on whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Carbohydrate Counting: Monitoring carbohydrate intake can help manage blood sugar levels, especially for those with diabetes. Understanding how different types of carbohydrates affect blood sugar is crucial.
- Glycemic Index: The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Low-GI foods cause slower, more gradual increases in blood sugar and are generally healthier choices.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help manage blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake by muscles. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercise (like walking or cycling) and resistance training (like weight lifting).
Medication and Insulin
For those with diabetes, medication or insulin therapy may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels. It's essential to follow healthcare provider recommendations and adjust doses as needed based on blood sugar monitoring.
Stress Management
Managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar control.
Sleep Hygiene
Prioritizing good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment, can positively affect blood sugar regulation.
Emerging Technologies and Future Directions
Advancements in technology are continually improving blood sugar management. Some emerging technologies and trends include:
- Advanced CGMs: Newer models of continuous glucose monitors are becoming more accurate and user-friendly, providing better insights into blood sugar patterns.
- Automated Insulin Delivery Systems: Also known as "artificial pancreas" systems, these combine CGMs and insulin pumps to automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar readings.
- Smartphone Apps: Various apps can help track blood sugar levels, diet, exercise, and medication, providing personalized insights and recommendations.
- Telehealth: Remote monitoring and virtual consultations with healthcare providers are making diabetes management more accessible and convenient.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. By focusing on a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and proper sleep, individuals can maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. With ongoing advancements in technology, managing blood sugar is becoming more convenient and effective, empowering individuals to take control of their health.
Whether you have diabetes, are at risk, or simply want to maintain optimal health, staying informed and proactive about blood sugar management can lead to a healthier, more vibrant life. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.






0 Comments